Launch of 'AI Security Portal' Utilizing New Classification Technology by LLM
―Facilitates broad access to and centralized dissemination of the latest AI security information, contributing to rapid risk countermeasures―
KDDI Corporation
KDDI Research, Inc.
On March 26, 2025, KDDI Corporation and KDDI Research developed and launched a new classification technology utilizing large language models (LLM) and have launched a portal website, "AI Security Portal" (hereinafter, this is called "this site"), which consolidates and disseminates information related to AI security. This site systematically organizes the latest AI security information, enabling users to access the most up-to-date information they need.
Based on the "AI R&D and Utilization Principles for KDDI Group" [![]() 1], both companies are advancing research and development related to AI security. This site organizes, classifies, and consolidates the latest information available online about not only attack and defense methods against AI itself but also the impacts on people and society, along with countermeasure technologies for addressing those impacts.
1], both companies are advancing research and development related to AI security. This site organizes, classifies, and consolidates the latest information available online about not only attack and defense methods against AI itself but also the impacts on people and society, along with countermeasure technologies for addressing those impacts.
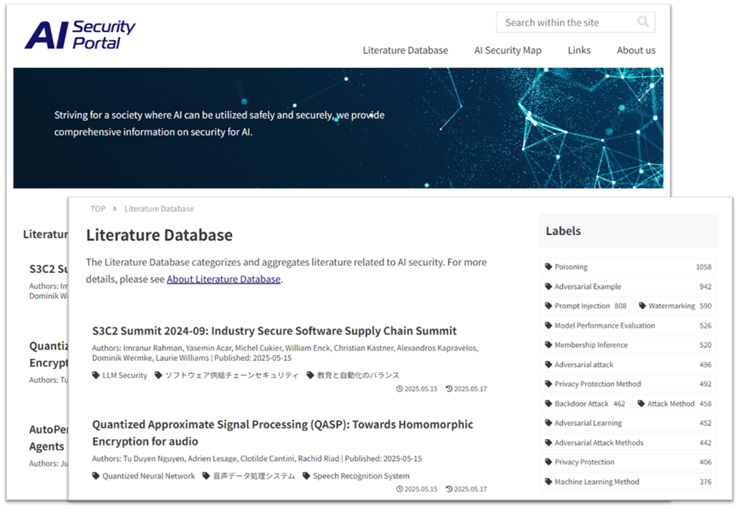
We developed and implemented a new classification technology [![]() 2] that utilizes LLM to categorize the vast amount of literature related to AI security available on the web. This technology automatically assigns appropriate labels to literature such as research papers published daily online, making it easier to organize and understand. (Patent pending) As a result, it becomes possible to organize and classify the latest AI security information that was previously unorganized. Additionally, new literature is continuously added to the site's database, enabling users to easily access the most up-to-date information they need.
2] that utilizes LLM to categorize the vast amount of literature related to AI security available on the web. This technology automatically assigns appropriate labels to literature such as research papers published daily online, making it easier to organize and understand. (Patent pending) As a result, it becomes possible to organize and classify the latest AI security information that was previously unorganized. Additionally, new literature is continuously added to the site's database, enabling users to easily access the most up-to-date information they need.
■Background
In recent years, as AI has become more widely implemented in society, concerns about attacks and misuse―such as backdoor attacks that cause AI to malfunction only in response to specific inputs, and prompt injection that leads LLMs to produce unintended responses―have increased. As a result, there is active discussion among experts regarding security technologies for identifying, assessing, and controlling risks, including vulnerabilities within AI systems.
Since AI security is a new research field, there is limited systematically organized information, and it is necessary to consolidate a wide range of papers and research and development trends from various perspectives in AI and security research. To enable all individuals to utilize AI safely, an environment that provides timely and appropriate access to the latest knowledge and technical information related to AI security is required. The government is promoting the establishment of AI security technologies necessary for a data-driven economy and society permeated by AI, under the Key and Advanced Technology R&D through Cross Community Collaboration Program (K Program) [![]() 3].
3].
The KDDI Group formulated the " AI R&D and Utilization Principles for KDDI Group " in 2021 to further enhance customer experience value through AI and contribute to the sustainable development of society. The Group is actively working to create an environment where all people can use AI safely. In May 2024, KDDI participated in the AI Governance Association (headquarters: Chuo-ku, Tokyo; Representative Directors: Koujin Ohsiba, Masashi Namatame, Hiroki Habuka, currently: General Incorporated Association AI Governance Association), which promotes the social implementation of AI governance and strengthens collaboration with policy makers [![]() 4]. Additionally, in February 2025, KDDI announced its participation in the "Reporting Framework," a method for AI development companies and others to verify and report their compliance with international codes of conduct established within the "Hiroshima AI Process," an international framework for forming rules on generative AI [
4]. Additionally, in February 2025, KDDI announced its participation in the "Reporting Framework," a method for AI development companies and others to verify and report their compliance with international codes of conduct established within the "Hiroshima AI Process," an international framework for forming rules on generative AI [![]() 5].
5].
■Information provided on This Site
This site comprehensively provides information related to AI security, including an overview of AI security, individual explanatory articles, literature information, news and event updates, and related websites. Users can access the latest information on AI security through this site.
Additionally, because the negative impacts resulting from attacks or misuse of AI are systematically organized as an AI Security Map, users can understand the scope of the influence that attacks on AI may have on people and society, thereby contributing to the development of countermeasures.
■Features and Structure of This Site
KDDI Research has established a knowledge aggregation environment to efficiently collect and organize information related to AI security available on the web by systematizing knowledge and technologies, in order to consolidate and provide information on AI security.
- Systematization of knowledge and technical information (Creation of an AI Security Map)
To organize and classify the increasing amount of AI security information resulting from advancements in AI technology, it is necessary to systematize related knowledge and technical information. To respond to this requirement, we conducted research on the elements of negative impacts that AI can have on society and people as a result of attacks or misuse, including not only attack and defense methods against AI itself (information system aspect) but also issues that had not been systematically organized until now, such as rights infringements like privacy violations and copyright issues (external influence aspect). Based on these findings, we created an AI Security Map that organizes the relevance of AI security information.
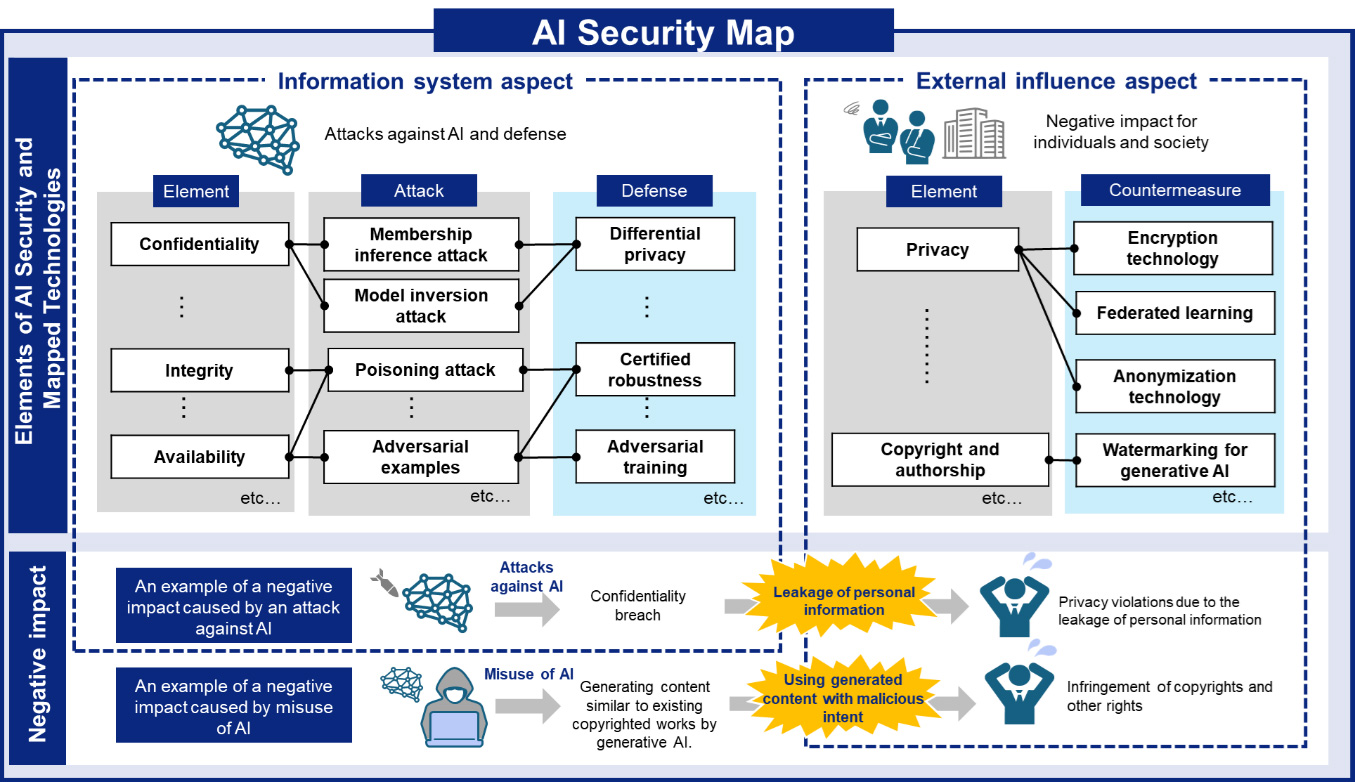
<Overview of the AI Security Map>
- Development of an information collection and classification platform
For this site, we developed a platform to classify and aggregate the vast amount of information related to AI security available on the web, including research papers, academic conferences, blogs, and social media. This platform incorporates the development and implementation of new classification techniques utilizing LLM.
Conventional classification methods face challenges such as the difficulty of collecting large quantities of high-quality training data [ 6] when training AI models, and the inability to assign appropriate labels to unknown literature not present in existing databases. The classification technology developed in this project addresses these issues by employing a search extension method based on a small amount of labeled data [
6] when training AI models, and the inability to assign appropriate labels to unknown literature not present in existing databases. The classification technology developed in this project addresses these issues by employing a search extension method based on a small amount of labeled data [ 7] and a few-shot prompting [
7] and a few-shot prompting [ 8], which generates new labels when inputting data into the LLM. This approach enables labeling of both existing and new literature.
8], which generates new labels when inputting data into the LLM. This approach enables labeling of both existing and new literature.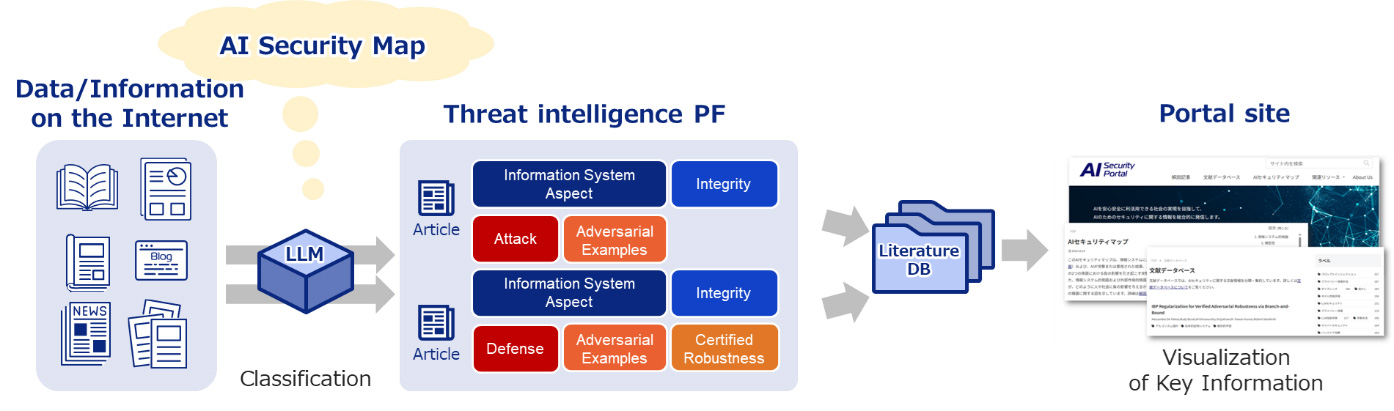
<Structure of this Site>
KDDI and KDDI Research will continue to promote the dissemination of AI security information, raise awareness, and encourage the spread of risk countermeasures to society.
This site is one of the outcomes of research and development conducted under the research theme "Systematization of knowledge and technologies for safe and secure AI utilization and the construction of a knowledge aggregation environment," which is part of the "AI Security Technology Establishment" project within Japan Science and Technology Agency's (JST) Strategic Innovation Program " Key and Advanced Technology R&D through Cross Community Collaboration Program (K Program)."
This achievement enables the comprehensive and rapid organization of the latest AI security techniques and knowledge, as well as the establishment of optimal risk communication methods [![]() 9] through high-precision automatic collection and classification. It contributes to realizing the research and development goal of accumulating essential knowledge on AI security and systematically organizing and acquiring the related knowledge and technologies.
9] through high-precision automatic collection and classification. It contributes to realizing the research and development goal of accumulating essential knowledge on AI security and systematically organizing and acquiring the related knowledge and technologies.
- [1]
- [2]Technology that utilizes LLMs to automatically assign document labels to academic papers and other documents.
- [3]
- [4]
- [5]
- [6]Data used to build and train machine learning and AI models.
- [7]Data that contains inputs and their corresponding correct outputs (labels) used for machine learning models to learn correct decisions.
- [8]A method of teaching AI models new tasks using only a small number of examples.
- [9]Sharing accurate information about risks among various stakeholders, such as experts and citizens.
- *The information contained in the articles is current at the time of publication.
Products, service fees, service content and specifications, contact information, and other details are subject to change without notice.
Downloads
